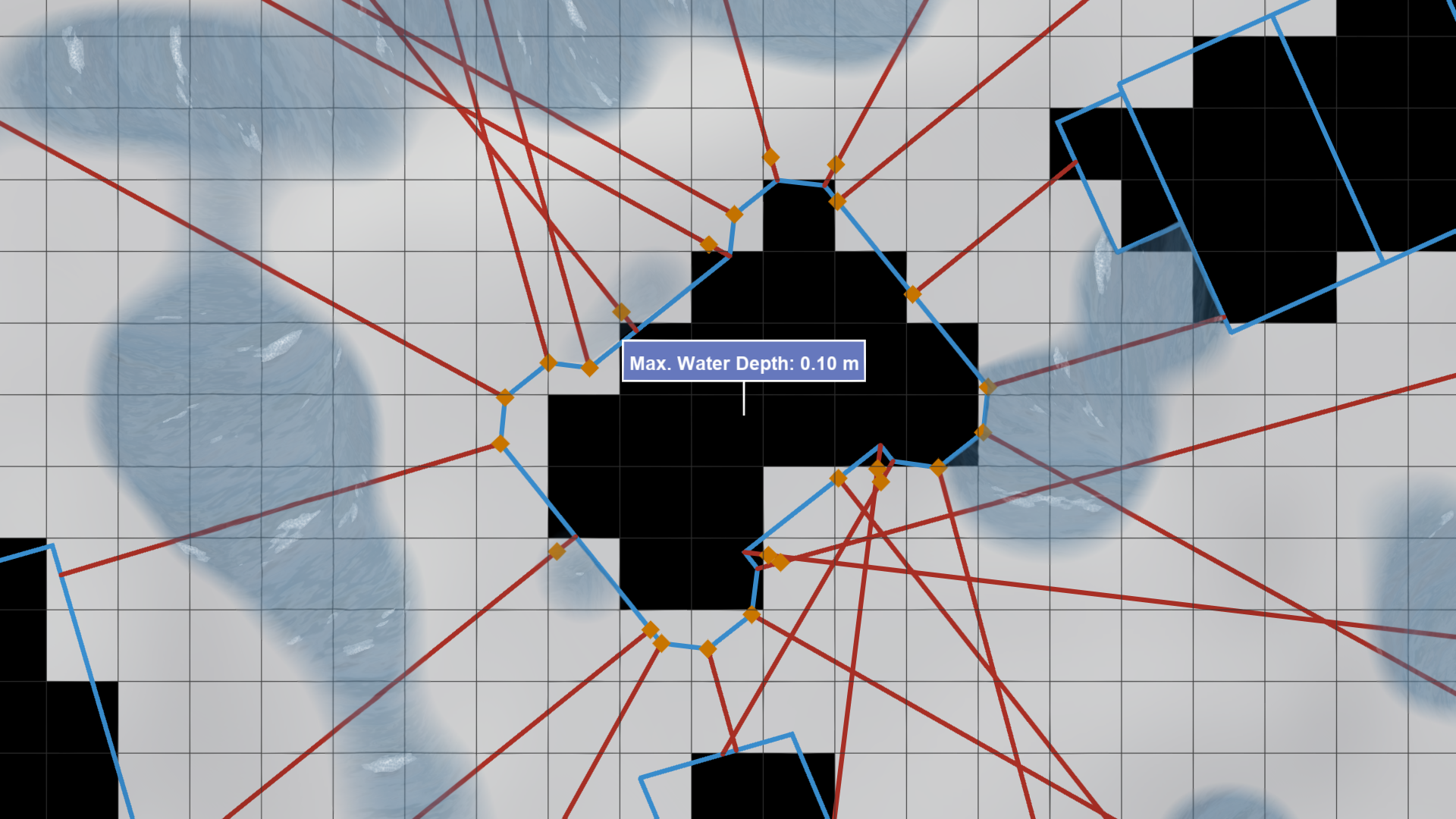
Building Water Depth Calculation
Building water depths are calculated using an algorithm that analyzes flood dynamics around each building. It considers multiple sampling positions along a building's façade and determines the maximum water depth among these samples. This method provides a robust measure of the water depth, regardless of the building's shape or the cell size of the simulation domain.

Hint: Explanatory visualizations of sampling positions and generated sampling lines can be enabled in the Building Inspection Action Tool Panel for selected buildings.
Algorithm Steps
-
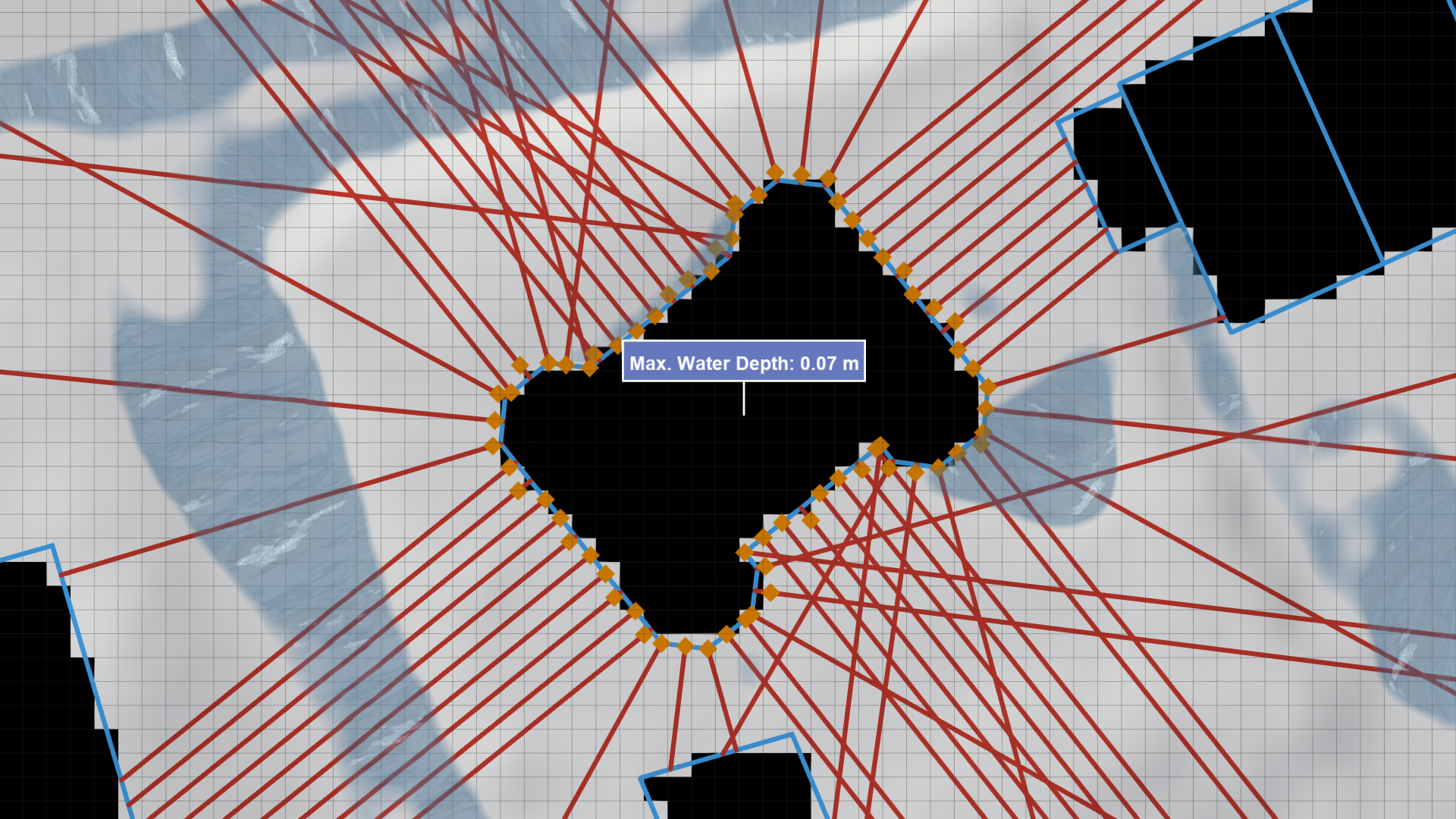
Sampling Line Generation: The algorithm generates sampling lines at all control points of the building's footprint polygon and at regular intervals along the segments connecting them. These lines (red lines in the image below) extend outward until they intersect with a building (including the same one) or reach a predefined maximum length.
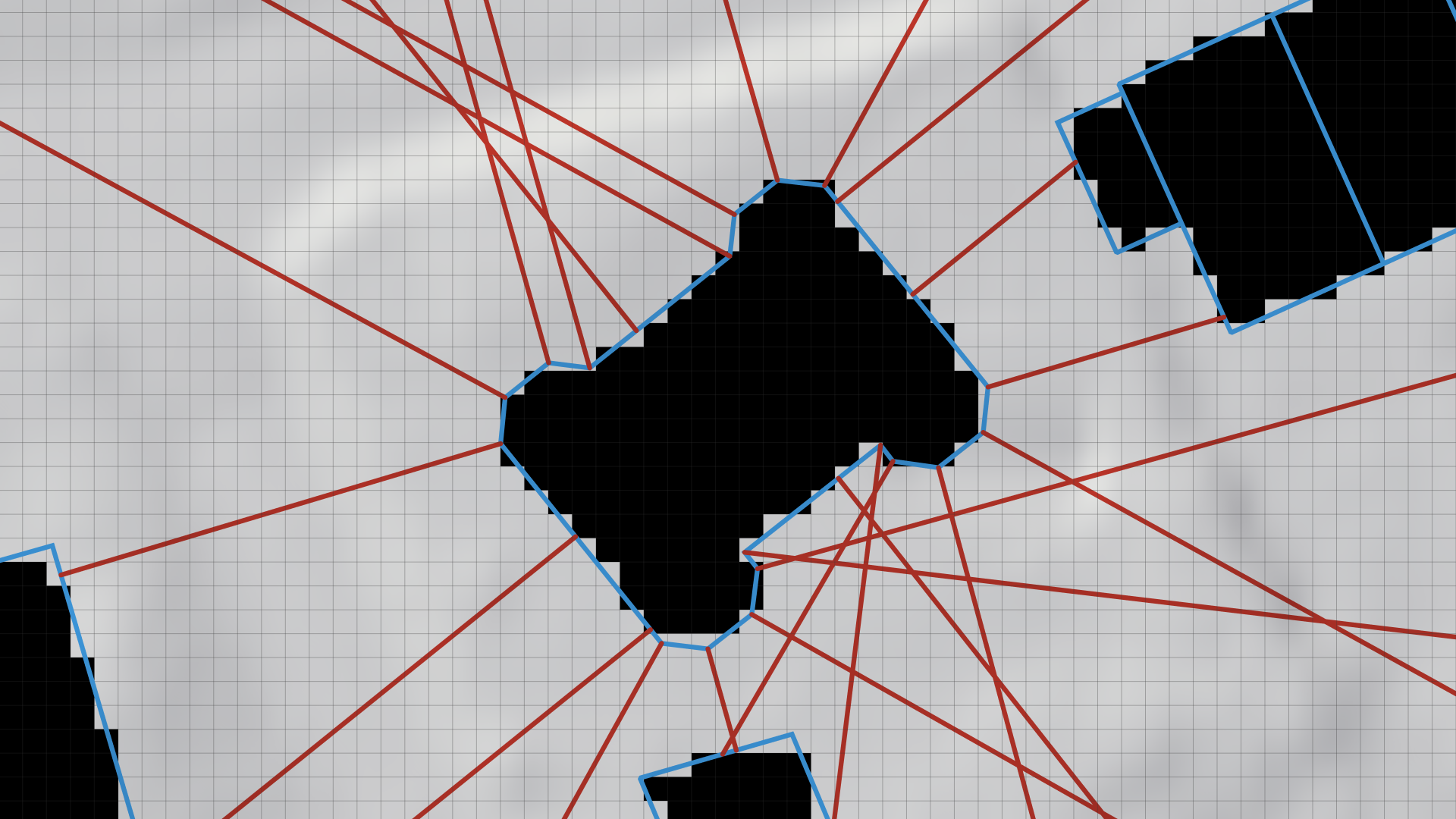
-
Sampling Position Selection: Along each generated line, the algorithm identifies the optimal sampling position that is nearest to the building façade without being inside a Wall Boundary cell. If a suitable position is found, it is added to the set of sampling positions for the building (orange squares in the image below).
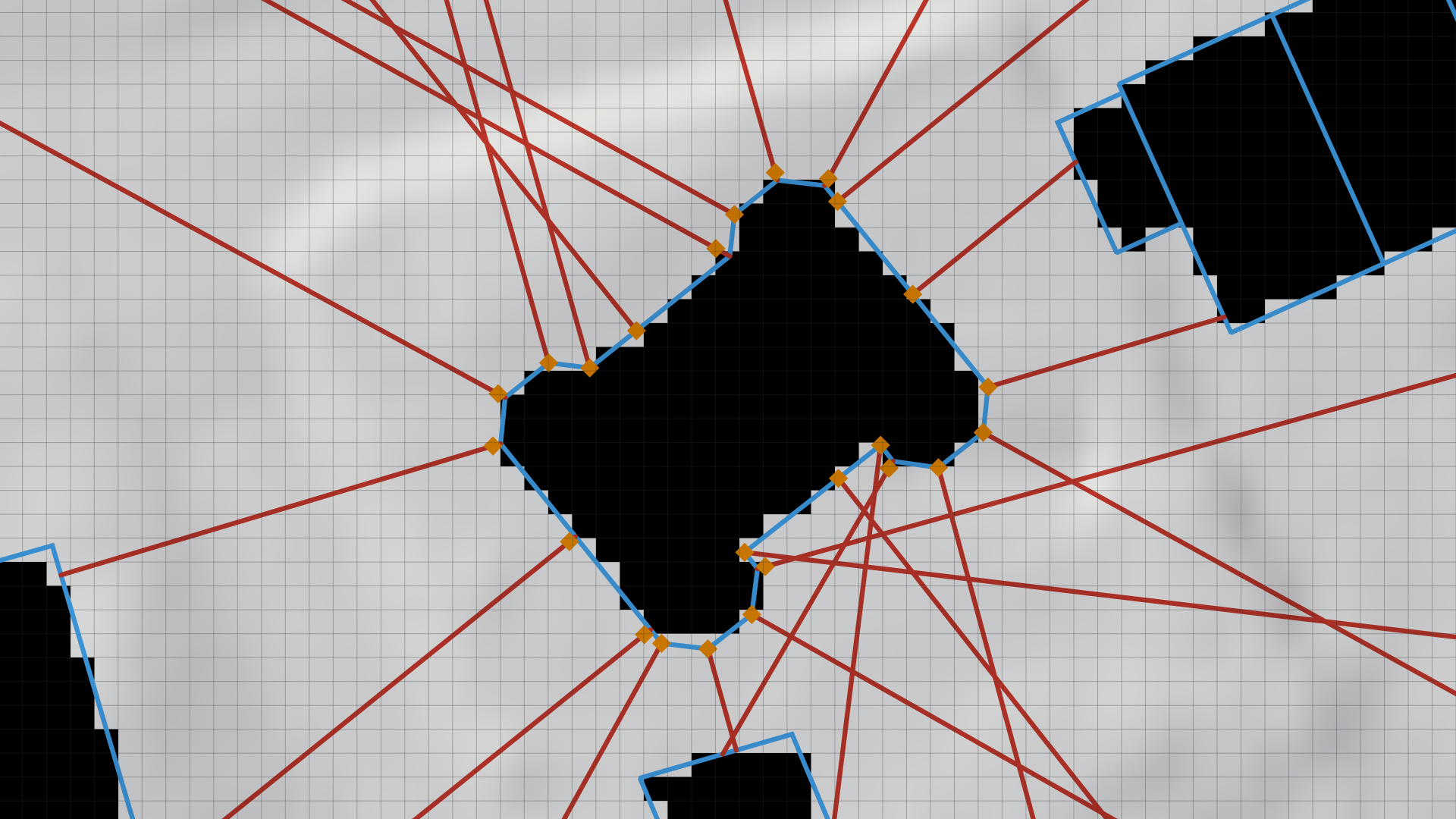
-
Water Depth Sampling The water depth output by the simulation is sampled at each identified sampling position. The maximum water depth recorded among all positions is selected as the final building water depth.
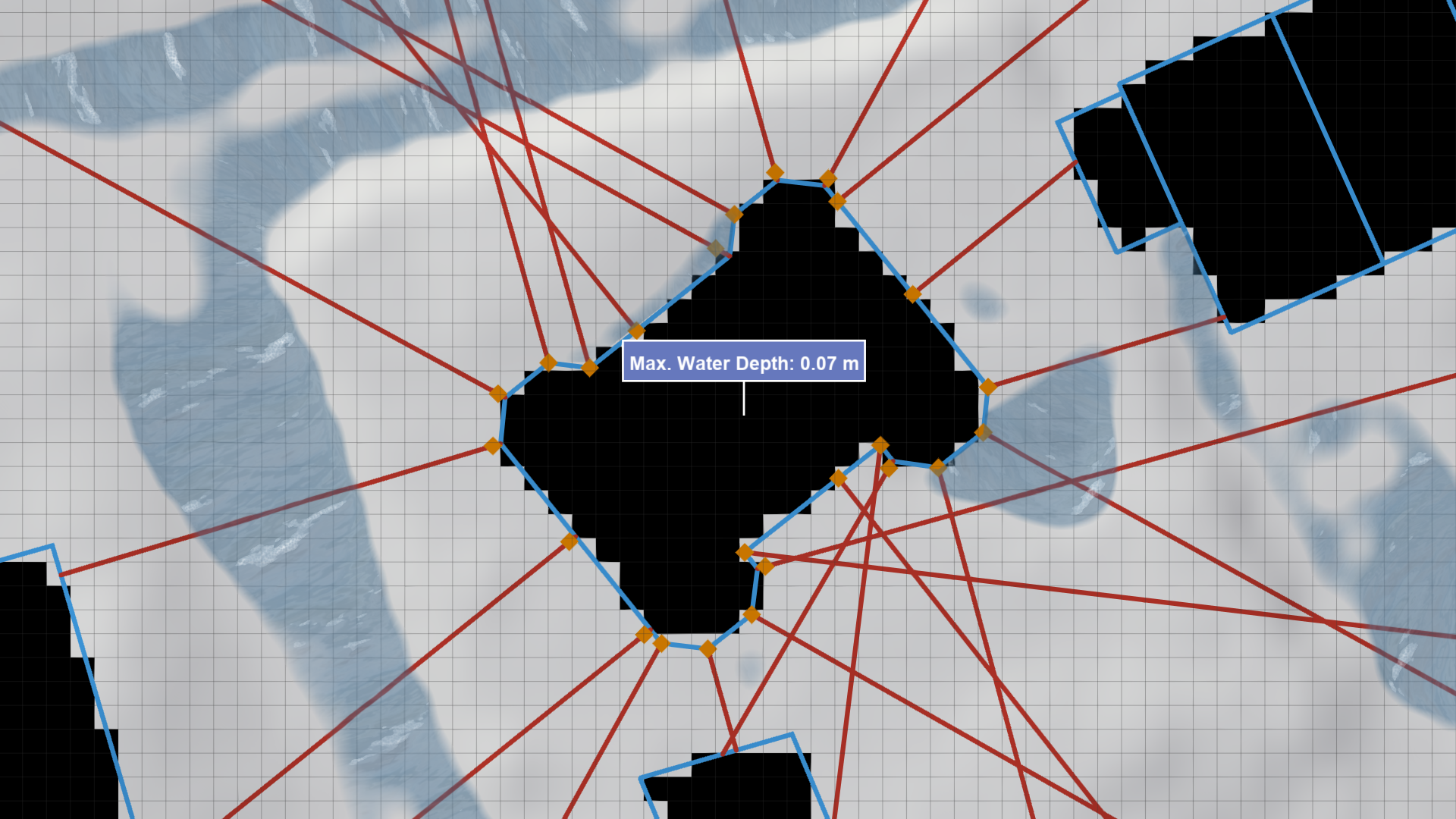
Remarks
Step Size Along Footprint
Sampling lines are generated at regular intervals along the footprint polygon. The interval size is controlled by the Step Size Along Footprint setting, which can be adjusted in the Visualization Layer section of the Visualization Settings Panel.
Reducing the step size results in more sampling lines, providing a more comprehensive sampling of water depths and enhancing the robustness of the building water depth calculation. Increasing the step size reduces the number of sampling operations, which improves system responsiveness for interactive tasks.

Hint: When exporting water depths for risk maps, the step size should be equal to or smaller than the cell size of the simulation domain.
Simulation Domain Dependency
Sampling positions depend on the size and locations of the simulation domain cells as well as on the presence and configuration of wall boundary cells.