Potential Damage Estimation with BEAM
BEAM (Basic European Asset Map) data provides spatially defined land uses and assets, making it a valuable tool for damage estimation when combined with floodplain maps. In scenarify, BEAM data can be intersected with simulation results to rapidly estimate potential damage within a given scenario.
BEAM data consists of polygons, each representing asset values across different categories like infrastructure, natural resources, industrial sites, entities, and land use. A detailed dataset for Germany can be accessed here and further explanations about damage estimation using BEAM can be found here. To estimate potential damage, BEAM polygons are rasterized onto the simulation grid. The maximum water depths are then intersected with these rasterized polygons using the algorithm explained below.
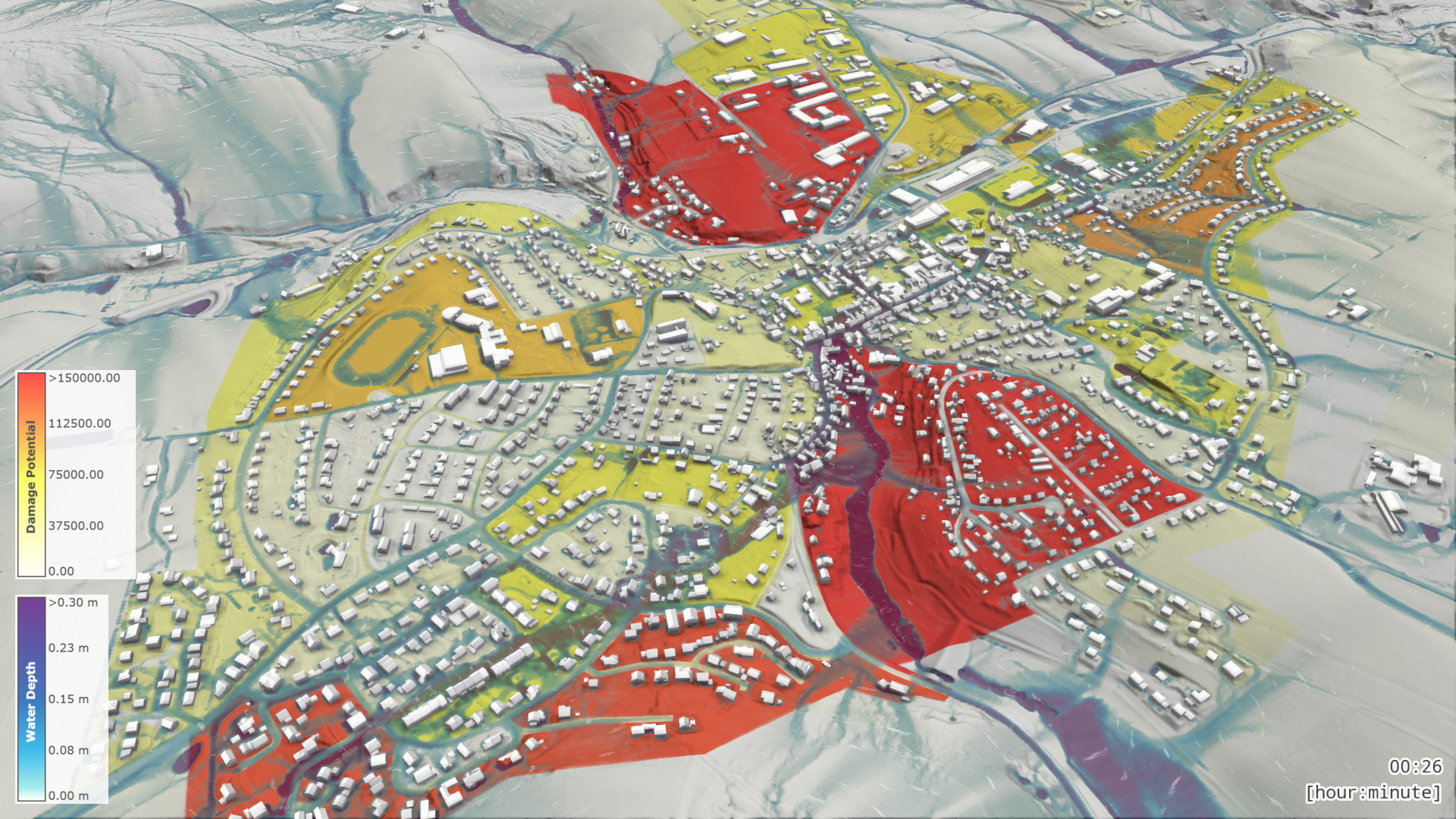
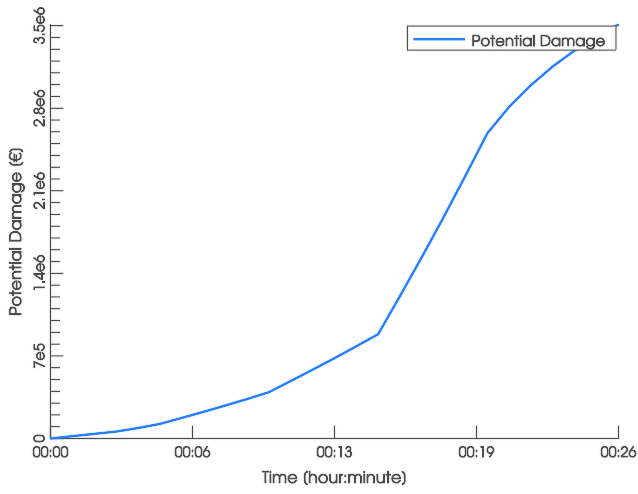
Results of the potential damage estimation can be visualized on the terrain with the Visual Preset Surface: Potential Damage, as illustrated above. The sum of all potential damages over time within the simulation domain can be displayed in the Plots & Charts Panel in the category Surface and Soil: Potential Damage.
BEAM algorithm
The BEAM algorithm calculates potential damage for each polygon in the dataset. BEAM includes damage functions that correlate water depth with damage grades. For each cell, the damage grade helps estimate total damage across all asset categories within a polygon. The damage calculation follows this formula:
where \(p\) is the current polygon, \(c\) is the current cell, \(k\) is the current category, \(v\) is the asset value of the current polygon and category, \(f\) is the damage function, \(b\) is the water depth, and \(A\) is the intersection area of the cell and the polygon. The total damage for each cell is the sum of damages across all categories:
Finally, the total damage for each polygon is calculated by summing the damage across all its cells: