Key Parameters Influencing Surface Runoff
Surface runoff is the portion of precipitation that is not intercepted by vegetation or infiltrated into the soil but instead flows over the land surface. Its formation is controlled by rainfall characteristics , interception, soil properties , topography, and land use. In urban areas, impermeable surfaces and sewer structures strongly modify runoff generation and flow paths. These factors together determine the volume, timing, and routing of surface runoff, making it a central process for hydrological modeling and flood risk assessment.
Baier et al. (2025) identified key parameters influencing surface runoff. Since rainfall is the primary driver of runoff generation, its characteristics, such as intensity, duration, and temporal pattern, have the strongest impact. Other important parameters include the representation of infiltration processes and the consideration of sewer networks. The coupling of roof water with sewer systems can further reduce surface runoff and significantly alter flow dynamics.In addition, changes to the parameters of these components strongly affect runoff generation. To a lesser extent, interception, the resolution of the simulation grid, and the treatment of impermeable areas also influence model results.
Some of these parameters and their effects are presented below. The screenshots were generated using the NRW base model. A base configuration was selected, and in each screenshot only the corresponding parameter was modified. For the base model, the KOSTRA rain choice is used, with a constant rainfall duration of 60 minutes at an intensity corresponding to SRI 7 (Starkregenindex) and assuming saturated infiltration.
We begin with rainfall settings. The rain type determines the rainfall pattern and can be specified in the Global Simulation Settings for the KOSTRA rain choice.
Block Rain represents a rainfall pattern with uniform intensity overthe entire rain duration, creating a steady and consistent input.
Euler Type II describes a stochastic rainfall pattern that models variable intensity and intermittent bursts, capturing more realistic storm behavior.
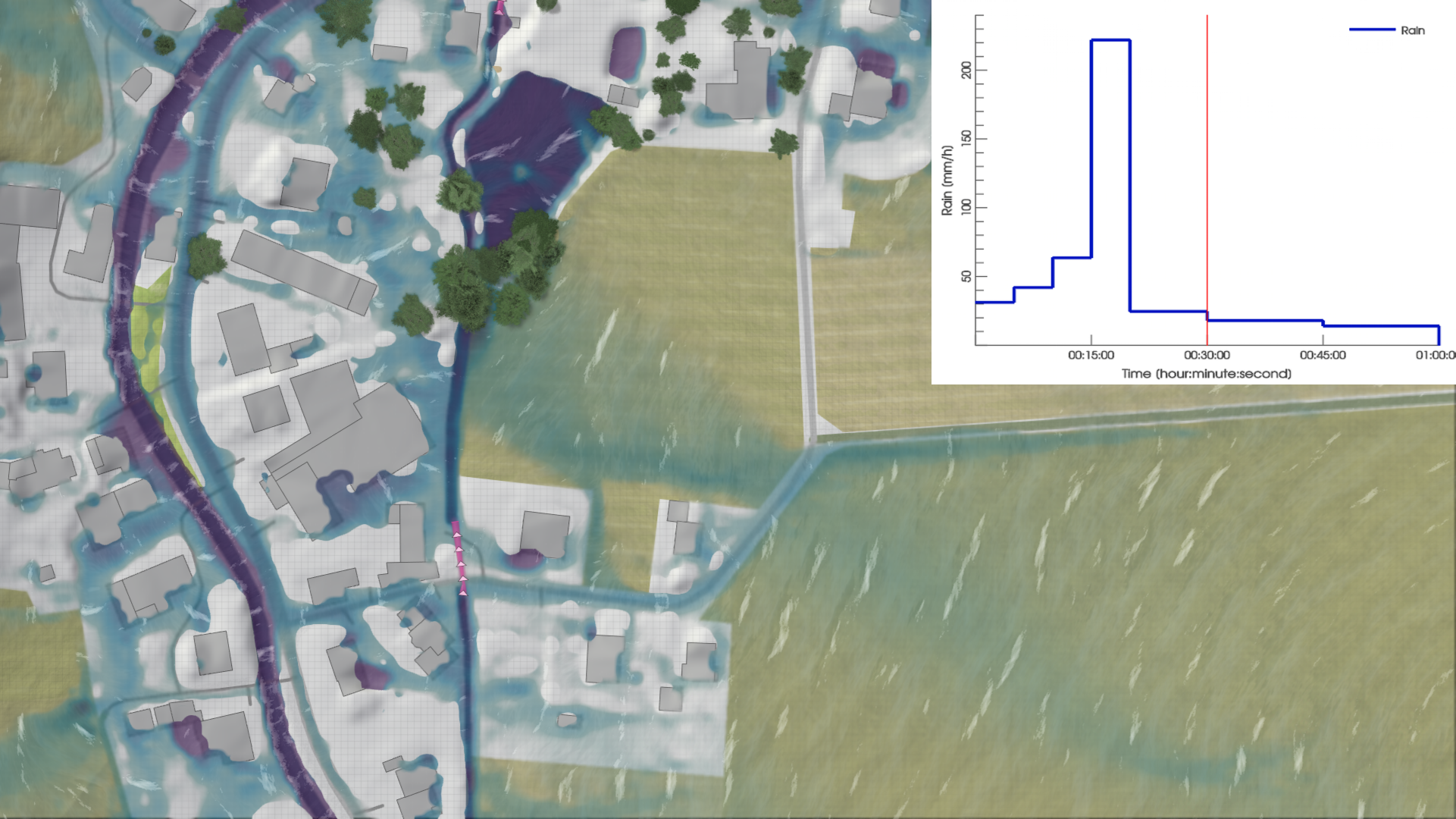
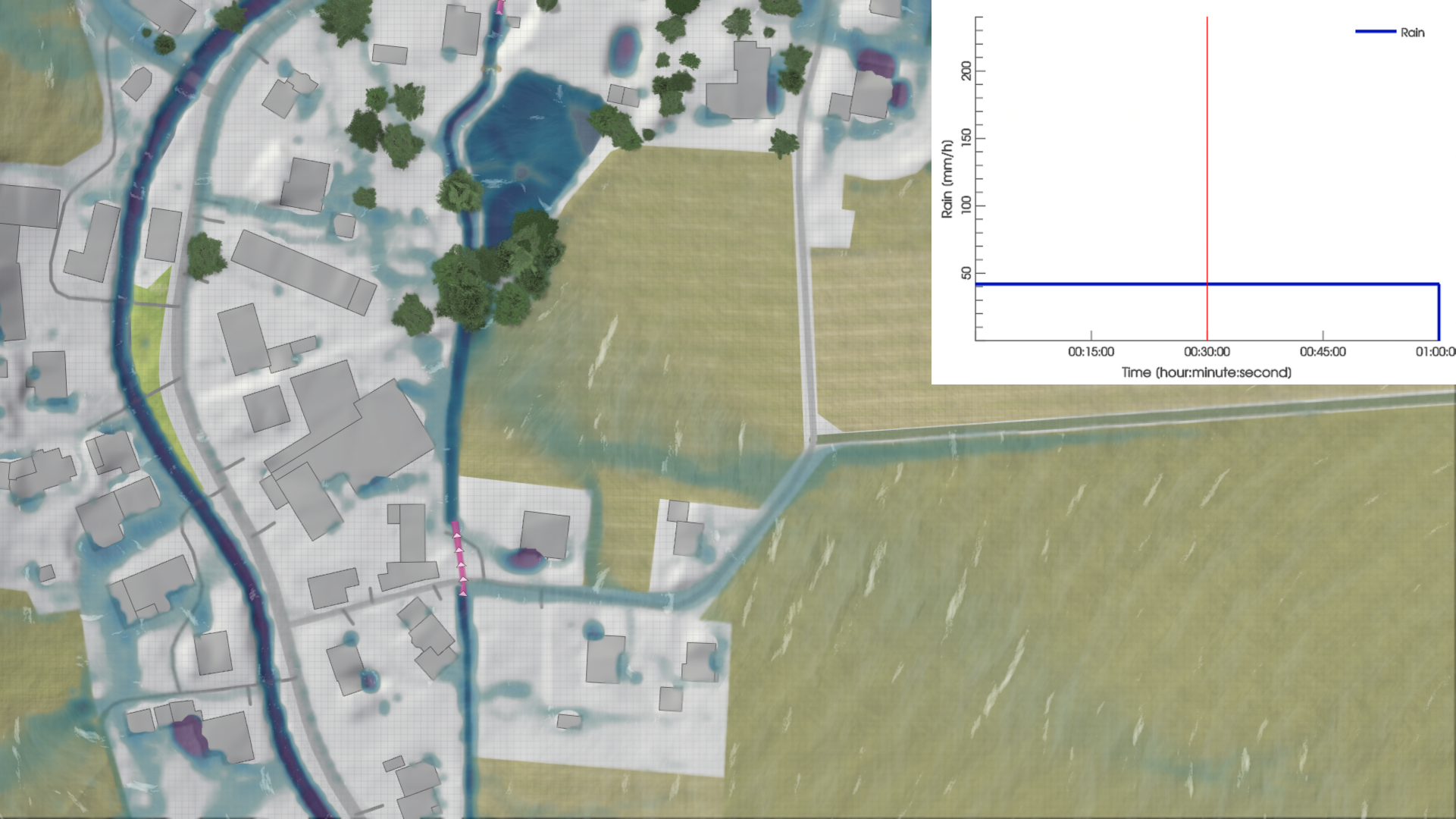
Rain duration can be modified in the same menu. Note that changing the duration does not alter the total precipitation volume, but only the distribution of rainfall rates.
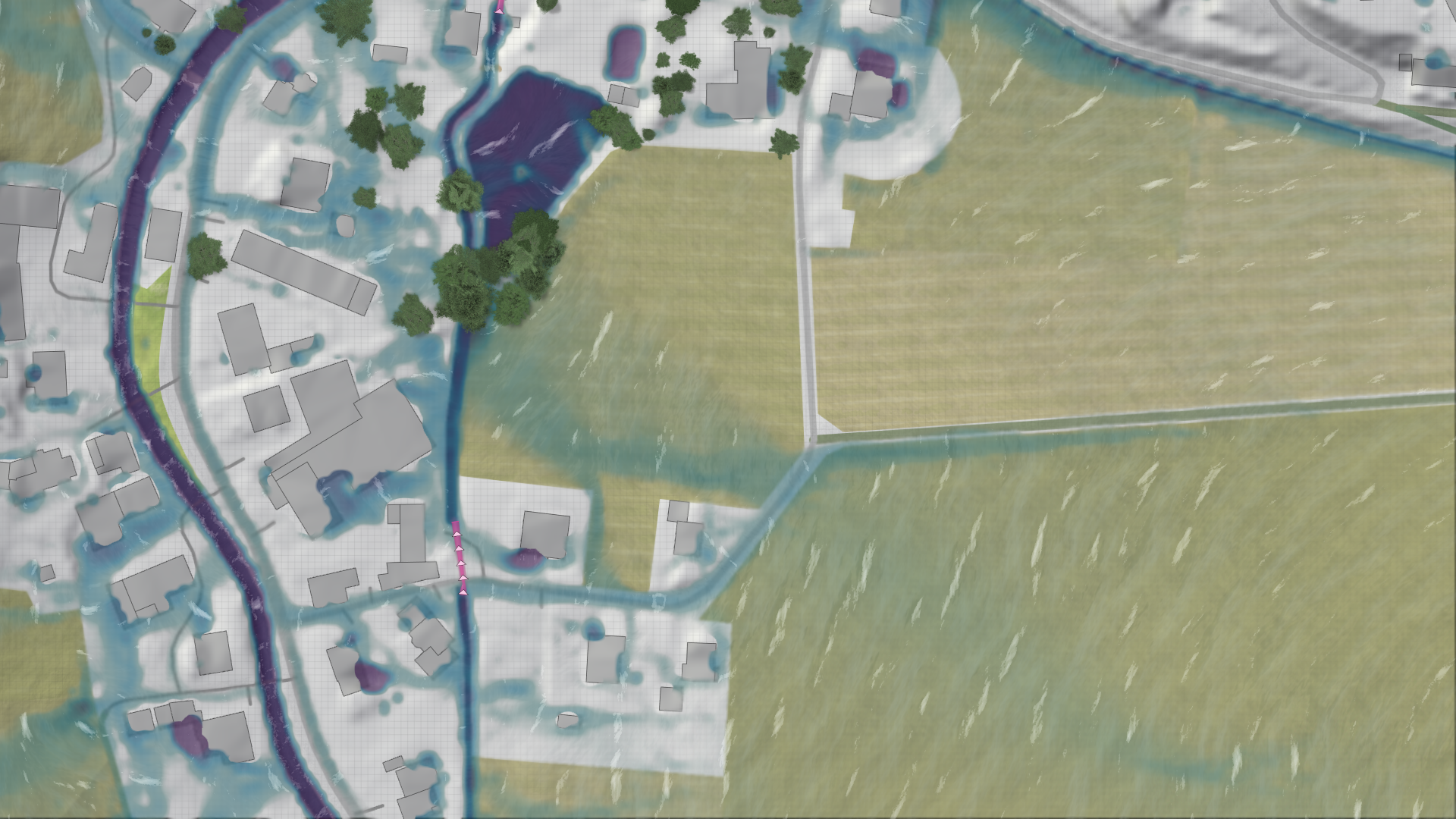

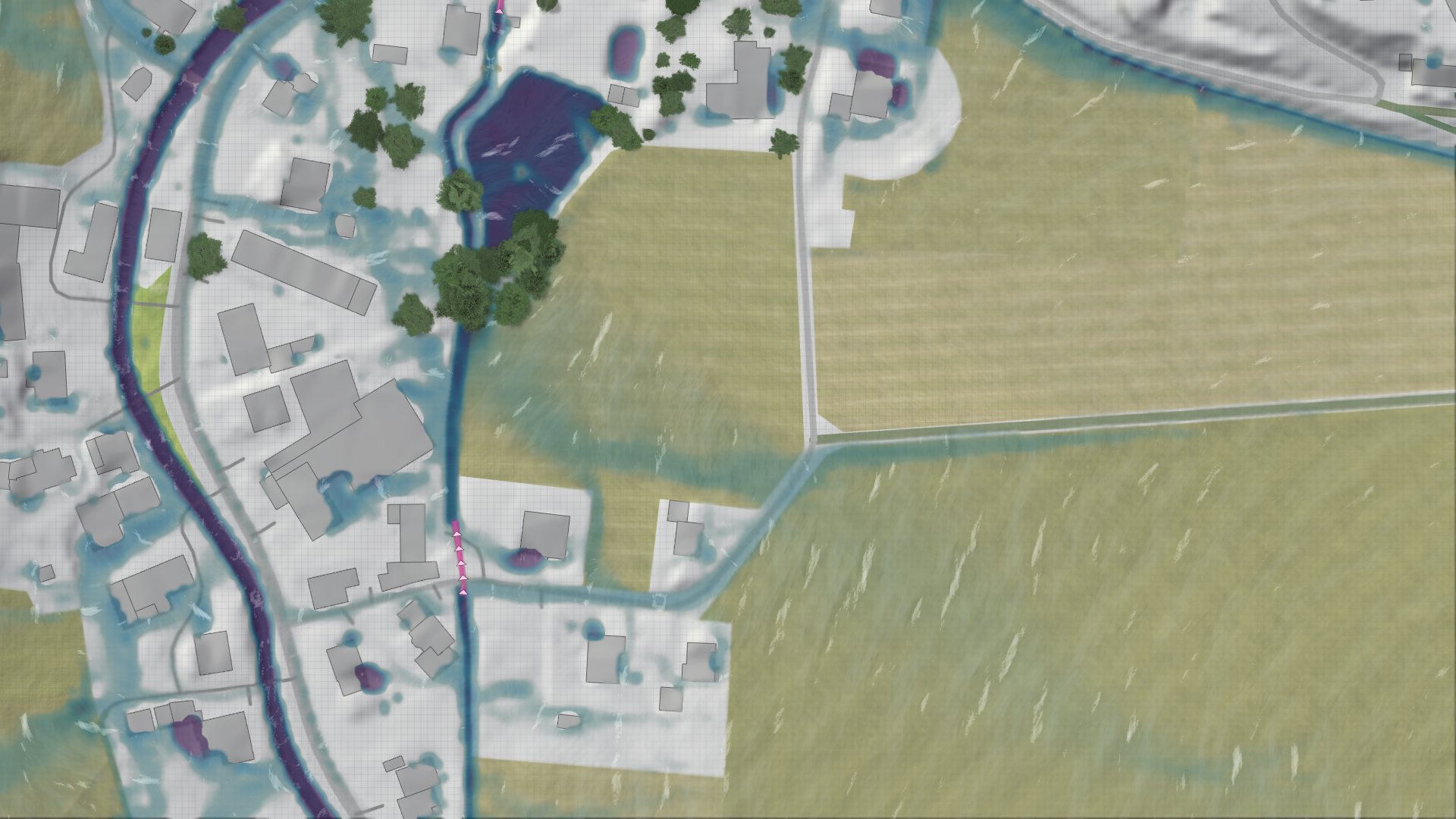
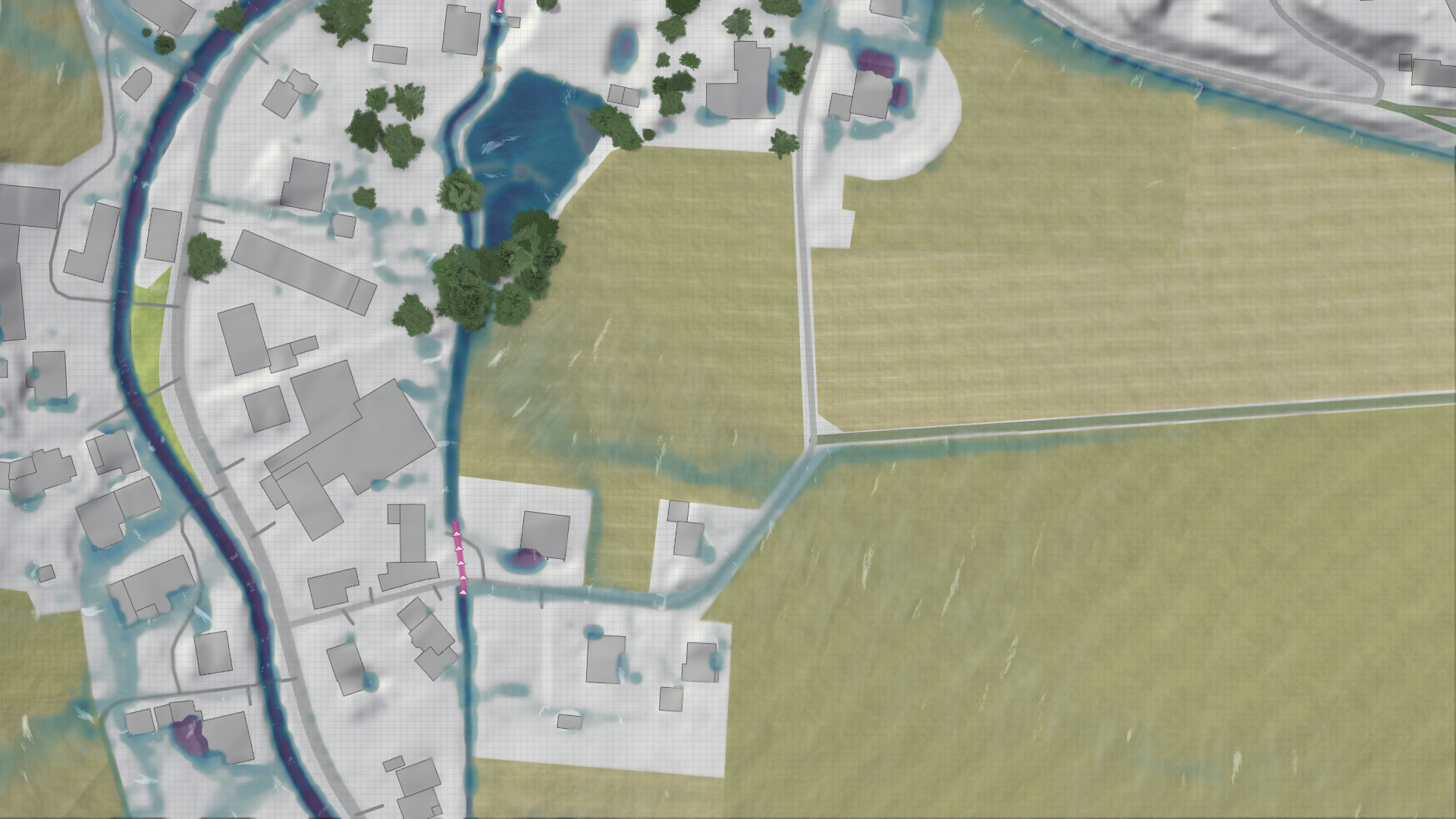
The rain intensity can be specified by the SRI (Starkregenindex) or the return period for the KOSTRA rain choice.
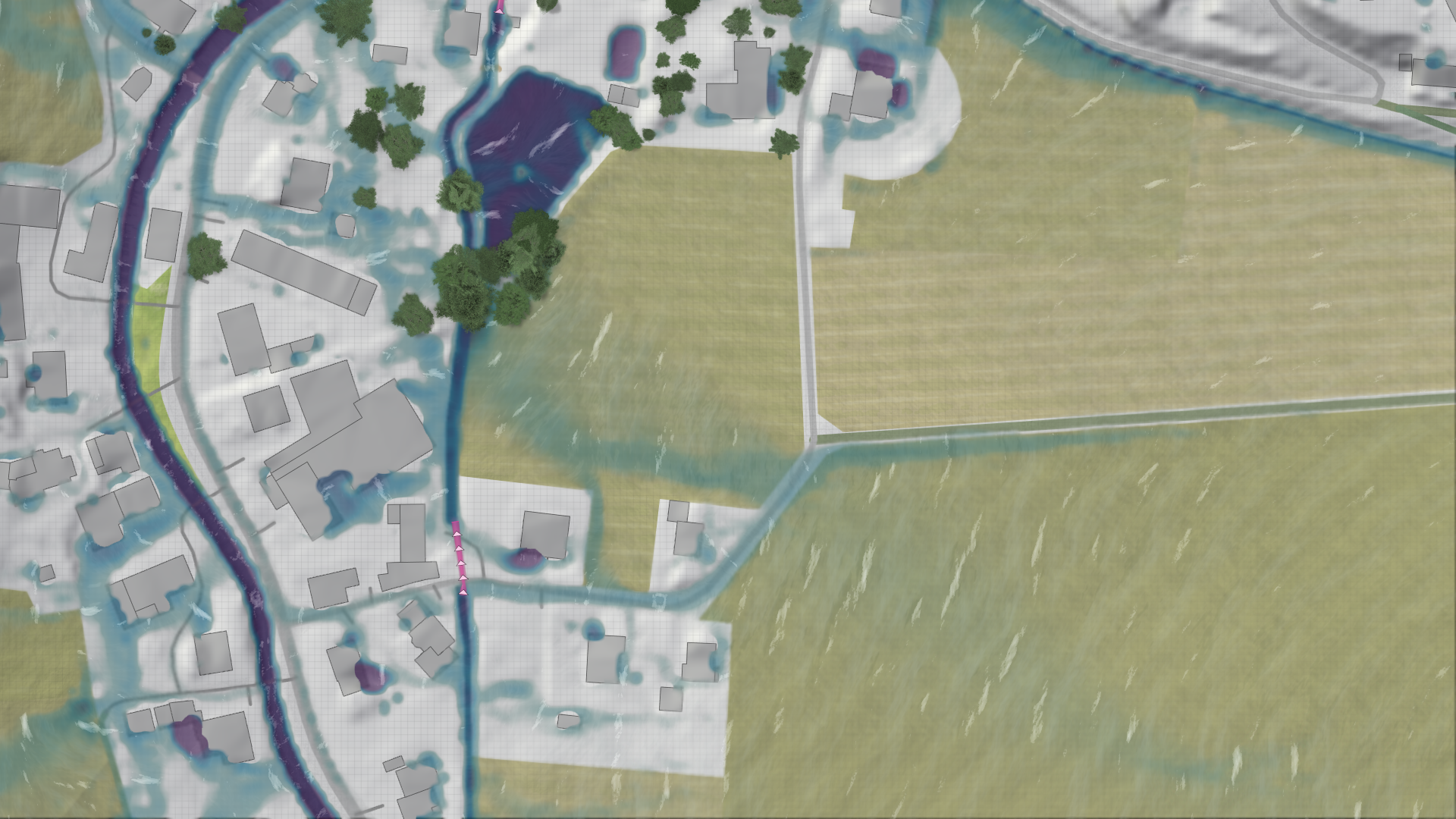

Another critical component for runoff generation is the infiltration model.
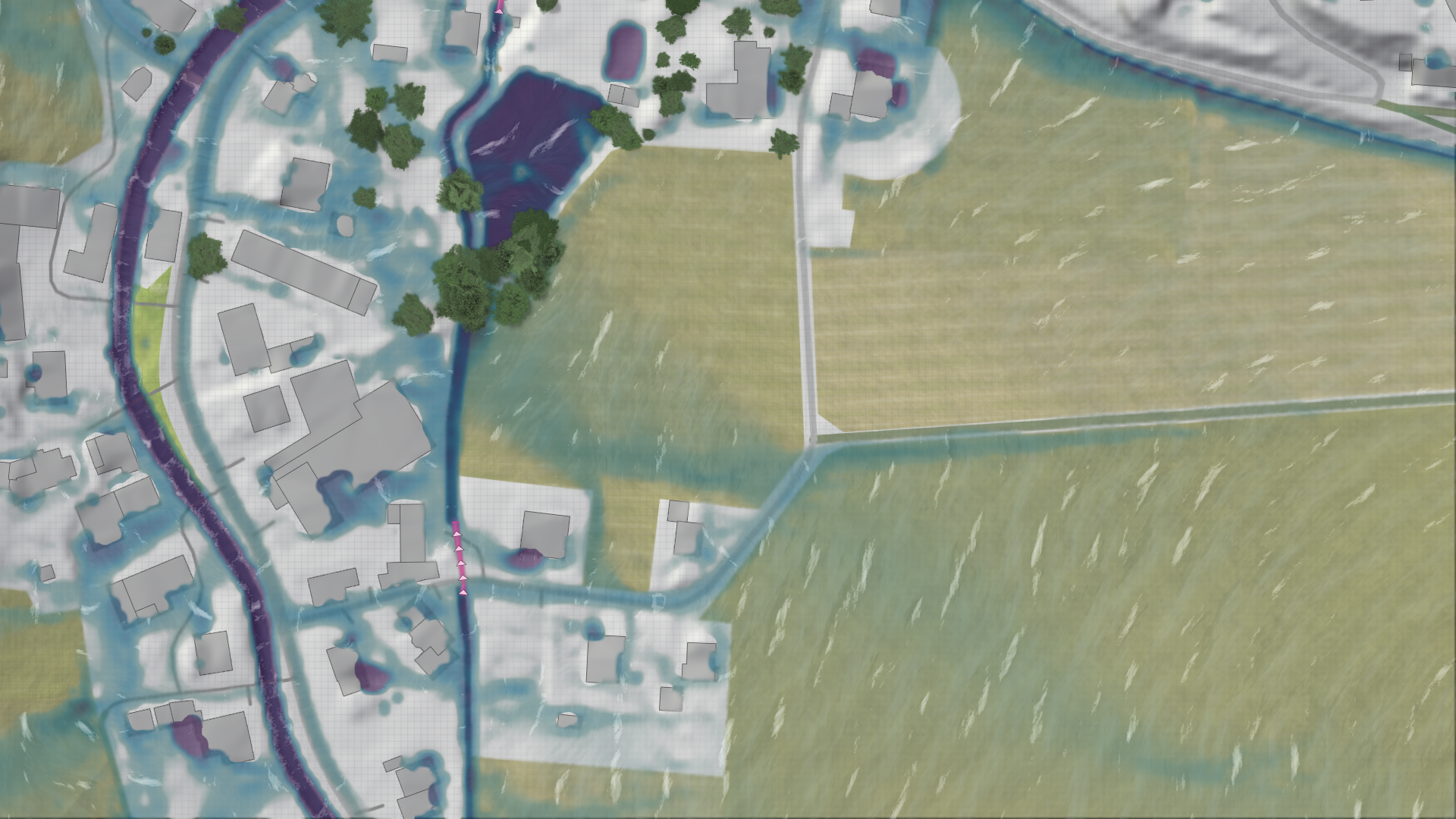
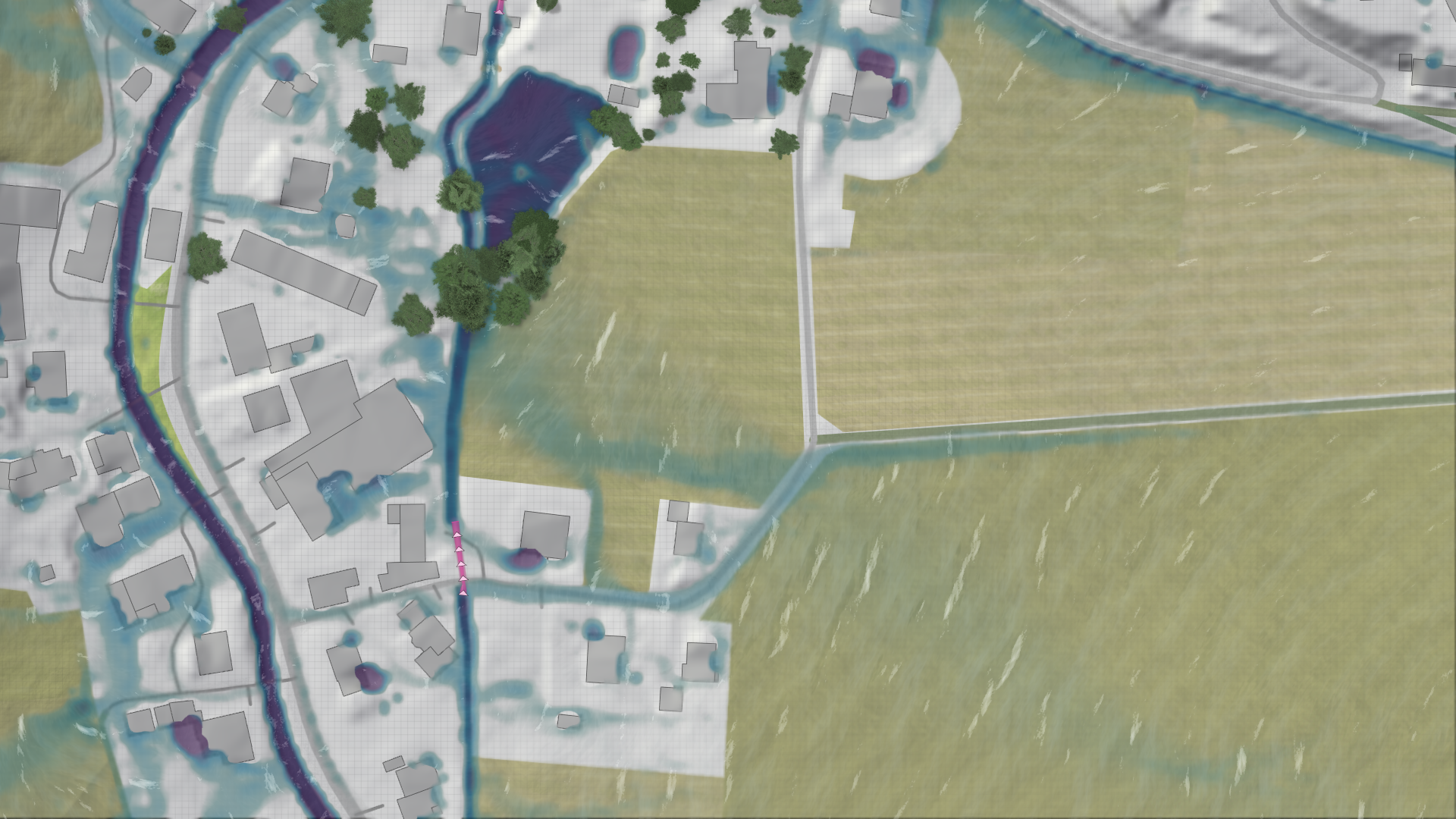
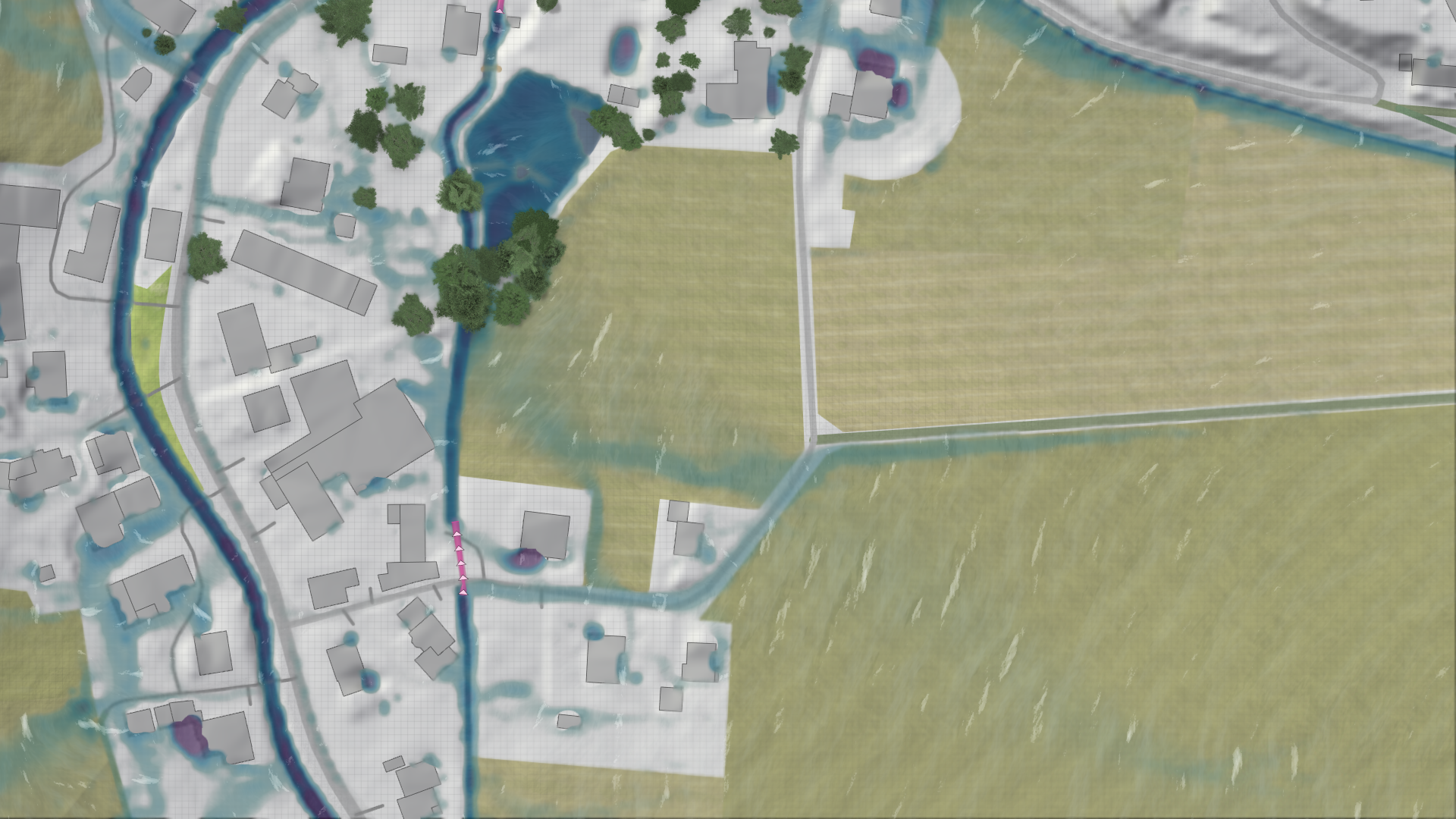



Infiltration parameters can be scaled to make the infiltration rates to fit to your scenario. These scalers can be found in the Global Simulation Settings under the infiltration model category.
References
Baier, A., Popp, L., Buttinger-Kreuzhuber, and Waser, J. 2025. Sensitivity analysis of detailed 1D-2D models for creating heavy rainfall hazard maps. Korrespondenz Wasserwirtschaft 06/25: 314–324.
DOI: 10.3243/kwe2025.06.001