Rain
Rainfall intensity is defined by a time- and space-dependent precipitation rate, which is then optionally reduced by interception resulting in an effective rain rate. Rain characteristics, such as intensity, duration, and temporal pattern, can be adhusted in the Global Simulation Settings.
Hint: A detailed guide on configuring rainfall is available here.
Precipitation
Visualize the rain time series as rain depths or rain rates in the Plots & Charts Panel:
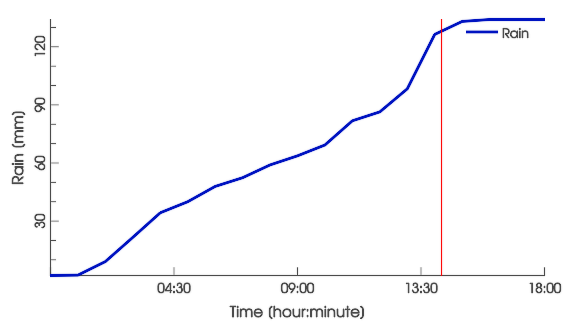
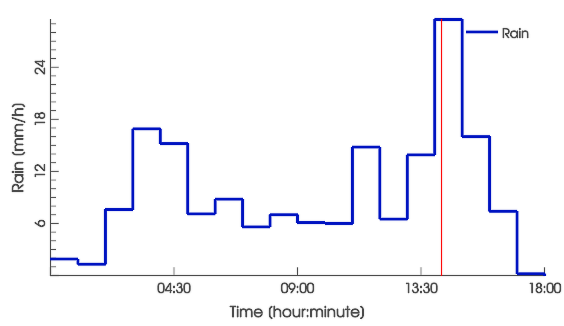
In scenarify, the rain can be defined in a spatially uniform or in a spatially distributed manner.
Spatially Uniform
For a uniform distribution of rainfall across the entire area, one can either enter the rate and duration of rainfall or specify the total amount and duration. Additionally, one can load rainfall data from a CSV file, where one can either specify precipitation rates or precipitation depth increments. Precipitation depths must be provided as increments between time values, rather than cumulative totals, and will be converted into rainfall rates. The rain rates are interpolated as a piecewise constant function.
Spatially Distributed
From KOSTRA: For KOSTRA rainfall data, one can either enter the Starkregenindex (SRI) or choose a return period. Specify the release, return period, amplification factor, precipitation type, and duration as required. Both a Euler-Typ-II and a temporally uniform rainfall distribution are supported.
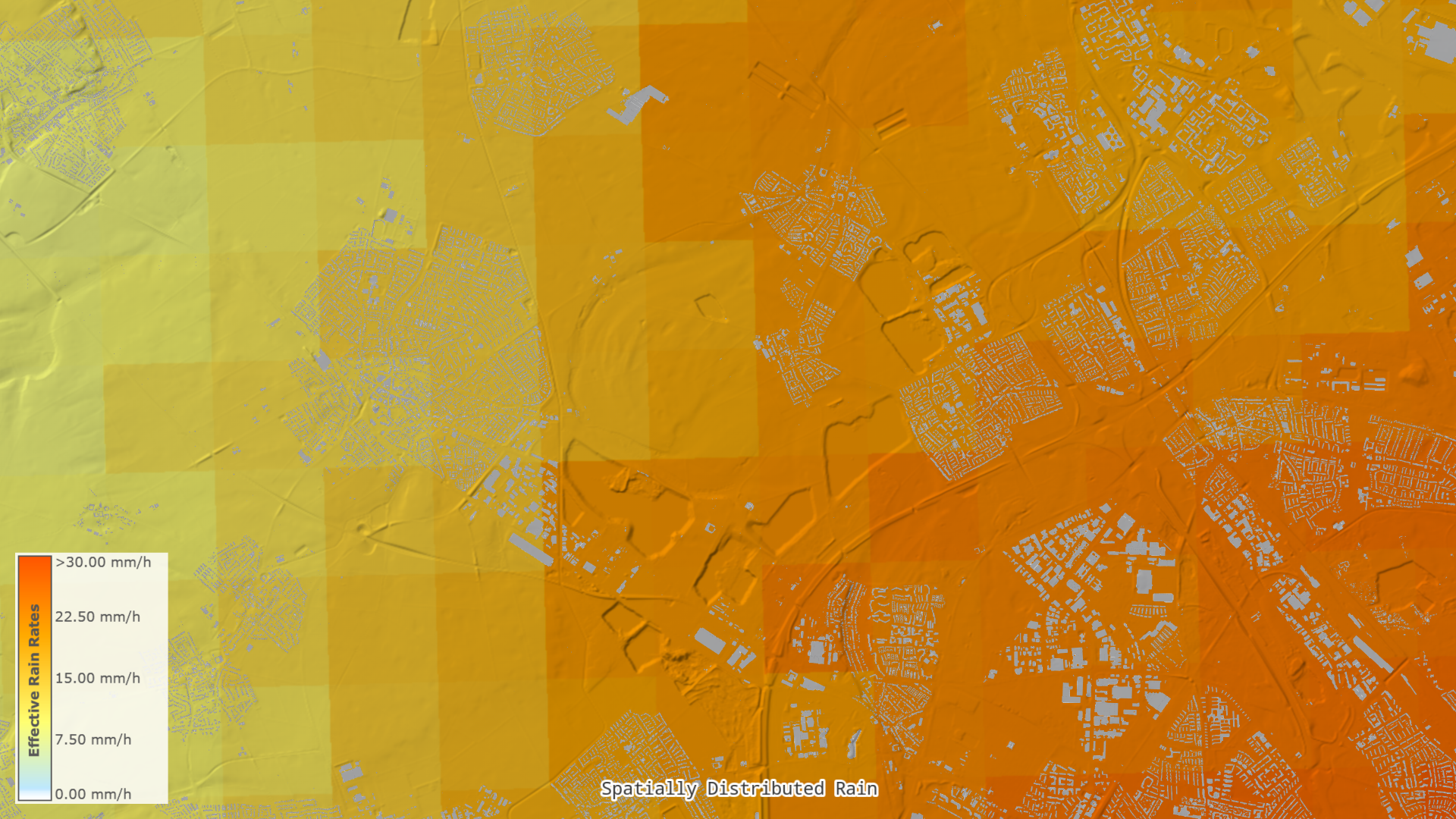

From Spatio-Temporal Data: Upload a sequence of files, where each file represents the spatially distributed precipitation at a specific time step. This method is particularly suited for:
- Radar-based precipitation measurements, recorded at a specific temporal resolution
- Pre-processed effective precipitation data, already accounting for infiltration or interception (e.g., as in the OAK files provided by Baden-Württemberg)
Learn More: A step-by-step guide—including freely available example data—for setting up rainfall from custom files can be found in the Advanced Setups section.
Interception
The spatially distributed runoff simulation integrates surface flow routing with interception to determine effective precipitation. The interception component reduces effective precipitation by accounting for micro-topographic depressions and vegetation losses. The two interception parameters:
- interception storage capacity \( I_S \), and
- interception rate \( i \)
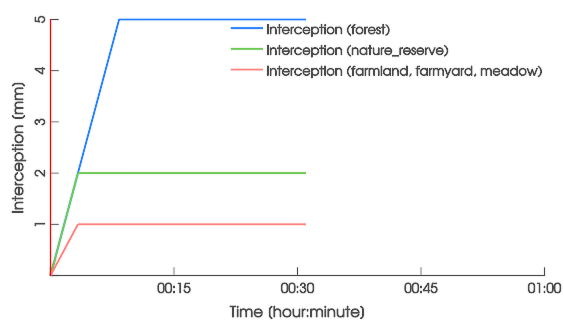
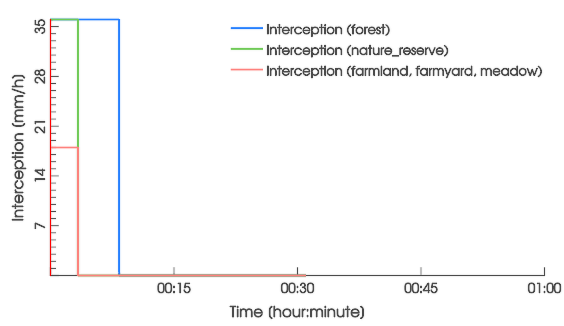
are usually set from land use. The interception storage capacity \( I_S \) is typically around 1 mm, except in forests where the default value is 5 mm.
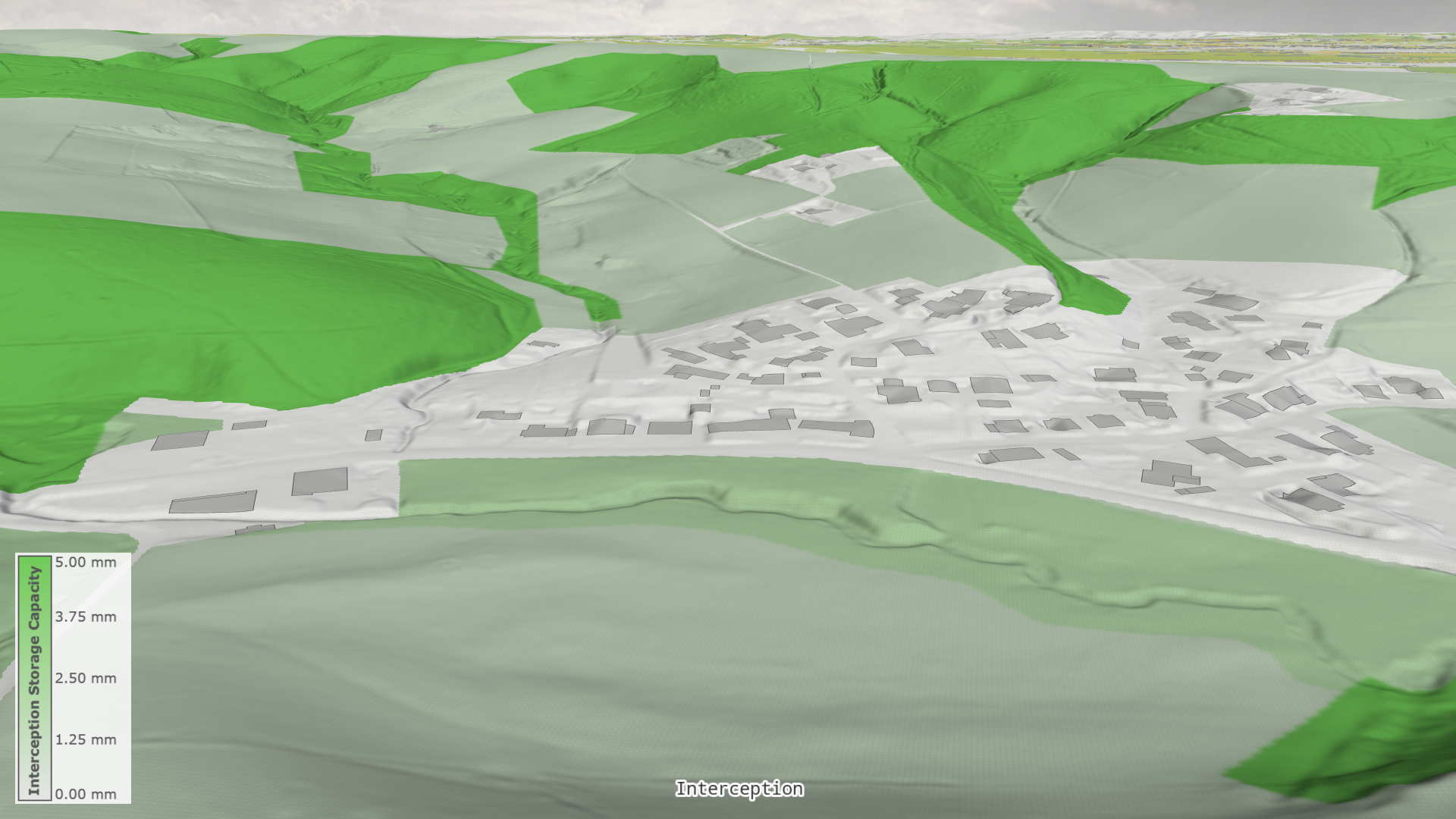
The cumulative interception \( I(t) \) up to time \( t \) is modeled with the constant non-negative interception rate \( i \) until the predefined storage capacity \( I_S \) is reached. The spatially distributed effective precipitation rate \( p_e(t) \) is thus given by reducing the precipitation rate \( p \):
Visualize the interception depths \( I(t) \) or the rates \( i(t) \) in the Plots & Charts Panel: